Foreign Function Interface¶
This sectioh shows how to wrap functions or classes from other languages to use in Python. We will only look at examples from C, C++, and Fortran. We will also look at calling R and Matlab functions via line and cell magics.
C¶
Using ctypes to wrap an R function from libRmath¶
R comes with a standalone C library of special functions and distributions, as described in the official documentation. These functions can be wrapped for use in Python.
Using cytpes¶
In [15]:
from numpy.ctypeslib import ndpointer
from ctypes import CDLL, c_int, c_double, POINTER
In [16]:
def rnorm(mu=0, sigma=1):
lib = CDLL('./libRmath.dylib')
lib.rnorm.argtypes = [c_double, c_double]
lib.rnorm.restype = c_double
return lib.rnorm(mu, sigma)
def dnorm(x, mean=0, sd=1, log=0):
lib = CDLL('./libRmath.dylib')
lib.dnorm4.argtypes = [c_double, c_double, c_double, c_int]
lib.dnorm4.restype = c_double
return lib.dnorm4(x, mean, sd, log)
In [17]:
plt.hist([rnorm() for i in range(100)])
pass
In [4]:
xs = np.linspace(-3,3,100)
plt.plot(xs, list(map(dnorm, xs)))
pass
Wrapping your own C function¶
This is rahter unusual - most times we would probably just use Cython or
numba to compile from Python to C rahter than write a standalone C
function.
C implementation file¶
In [9]:
%%file c_fib.c
double c_fib(int n) {
double tmp, a = 0, b = 1;
for (int i=0; i<n; i++) {
tmp = a;
a = a + b;
b = tmp;
}
return a;
}
Overwriting c_fib.c
Cython definition file¶
In [10]:
%%file cy_fib.pxd
cdef extern from "c_fib.h":
double c_fib(int n)
Overwriting cy_fib.pxd
Cython implementation file¶
In [11]:
%%file cy_fib.pyx
cimport cy_fib
def fib(n):
return cy_fib.c_fib(n)
Overwriting cy_fib.pyx
Standard way to build a Python module¶
In [12]:
%%file setup.py
from distutils.core import setup, Extension
from Cython.Build import cythonize
ext = Extension("cy_fib",
sources=["cy_fib.pyx", "c_fib.c"],
extra_compile_args=["-w"])
setup(name = "Fibonacci numbers",
ext_modules = cythonize(ext))
Overwriting setup.py
Acutally build the module¶
In [13]:
%%bash
python setup.py -q build_ext --inplace
Compiling cy_fib.pyx because it changed.
[1/1] Cythonizing cy_fib.pyx
In [14]:
import cy_fib
cy_fib.fib(10)
Out[14]:
55.0
C++¶
This is almost similar to C. We will use Cython to wrap a simple funciton.
In [23]:
%%file add.hpp
#pragma once
int add(int a, int b);
Overwriting add.hpp
In [24]:
%%file add.cpp
int add(int a, int b) {
return a+b;
}
Overwriting add.cpp
In [25]:
%%file driver.cpp
#include <iostream>
#include "add.hpp"
using std::cout;
using std::endl;
int main() {
cout << add(3, 4) << endl;
}
Overwriting driver.cpp
In [26]:
%%bash
g++ -o driver.exe driver.cpp add.cpp
./driver.exe
7
Fortran¶
If there is a message f2py not found, create a symbolic link to
f2py3 in the same directory.
In [38]:
%load_ext fortranmagic
The fortranmagic extension is already loaded. To reload it, use:
%reload_ext fortranmagic
In [39]:
%%fortran
subroutine fort_sum(N, s)
integer*8, intent(in) :: N
integer*8, intent(out) :: s
integer*8 i
s = 0
do i = 1, N
s = s + i*i
end do
end
In [40]:
fort_sum(10)
Out[40]:
385
In [41]:
%%fortran --link lapack
subroutine solve(A, b, x, n)
! solve the matrix equation A*x=b using LAPACK
implicit none
real*8, dimension(n,n), intent(in) :: A
real*8, dimension(n), intent(in) :: b
real*8, dimension(n), intent(out) :: x
integer :: pivot(n), ok
integer, intent(in) :: n
x = b
! find the solution using the LAPACK routine SGESV
call DGESV(n, 1, A, n, pivot, x, n, ok)
end subroutine
In [42]:
A = np.array([[1, 2.5], [-3, 4]])
b = np.array([1, 2.5])
solve(A, b)
Out[42]:
array([-0.19565217, 0.47826087])
R¶
In [45]:
%load_ext rpy2.ipython
In [47]:
%%R
options(warn=-1)
install.packages("igraphdata", repos = "http://cran.r-project.org")
library(igraph)
library(igraphdata)
data(macaque)
plot(macaque, layout=layout.auto, vertex.shape="circle",
vertex.size=8, edge.arrow.size=0.5, vertex.label=NA)
The downloaded binary packages are in
/var/folders/xf/rzdg30ps11g93j3w0h589q780000gn/T//RtmpdLdJIX/downloaded_packages
In [49]:
%%R
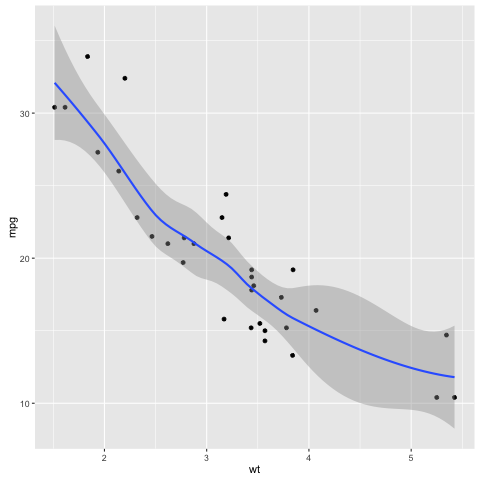
library(ggplot2)
ggplot(mtcars, aes(x=wt, y=mpg)) + geom_point() + geom_smooth(method=loess)
In [51]:
%R -o mtcars
In [52]:
mtcars.head(n=3)
Out[52]:
| mpg | cyl | disp | hp | drat | wt | qsec | vs | am | gear | carb | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mazda RX4 | 21.0 | 6 | 160 | 110 | 3.90 | 2.620 | 16.46 | 0 | 1 | 4 | 4 |
| Mazda RX4 Wag | 21.0 | 6 | 160 | 110 | 3.90 | 2.875 | 17.02 | 0 | 1 | 4 | 4 |
| Datsun 710 | 22.8 | 4 | 108 | 93 | 3.85 | 2.320 | 18.61 | 1 | 1 | 4 | 1 |
In [53]:
x = np.linspace(0, 2*np.pi, 100)
y = np.sin(x)
In [55]:
%%R -i x,y
plot(x, y, main="Sine curve in R base graphics")
Matlab¶
There is a similar interface to octave if you prefer open source.
In [1]:
%load_ext pymatbridge
Starting MATLAB on ZMQ socket ipc:///tmp/pymatbridge-054aea7d-c8d5-4d2f-8e0f-fd11618a184f
Send 'exit' command to kill the server
...........MATLAB started and connected!
/Users/cliburn/anaconda/envs/py35/lib/python3.5/site-packages/IPython/nbformat.py:13: ShimWarning: The `IPython.nbformat` package has been deprecated. You should import from nbformat instead.
"You should import from nbformat instead.", ShimWarning)
In [3]:
%%matlab
M = magic(5)
eigs(M)
M =
17 24 1 8 15
23 5 7 14 16
4 6 13 20 22
10 12 19 21 3
11 18 25 2 9
ans =
13.1263
-13.1263
21.2768
-21.2768
65.0000
In [4]:
n = 9
In [6]:
%%matlab -i n -o v
M = magic(n)
v = eigs(M)`a
M =
47 58 69 80 1 12 23 34 45
57 68 79 9 11 22 33 44 46
67 78 8 10 21 32 43 54 56
77 7 18 20 31 42 53 55 66
6 17 19 30 41 52 63 65 76
16 27 29 40 51 62 64 75 5
26 28 39 50 61 72 74 4 15
36 38 49 60 71 73 3 14 25
37 48 59 70 81 2 13 24 35
v =
369.0000
-118.4141
118.4141
-63.0069
63.0069
46.4758
In [7]:
v
Out[7]:
array([[ 369. ],
[-118.41407217],
[ 118.41407217],
[ -63.00687636],
[ 63.00687636],
[ 46.47580015]])
In [2]:
%%matlab
a = linspace(0.01,6*pi,100);
plot(sin(a))
grid on
hold on
plot(cos(a),'r')
Exercise
Wrap the rnorm and dnorm functions from the R standalone library
libRmath using cython instead of ctypes.
In [ ]: