
Research
Comparison of standard and fast-ping ADCP modes
NIDZIEKO, N. J., D. A. FONG, and J. L. HENCH, 2006. Comparison of Reynolds stress estimates derived from standard and fast-ping ADCPs. Journal of Atmospheric and Oceanic Technology, 23 (6): 854-861.
Abstract
A field experiment was conducted to directly compare the effect of different sampling modes on Reynolds stress estimates calculated from acoustic Doppler current profilers (ADCPs) and fast sampling acoustic Doppler velocimeters (ADV). Two 1.2 MHz ADCPs were deployed concurrently over a fortnightly cycle: one collected single ping measurements using mode 1 and a second ADCP employed the fast-ping rate mode 12 with subping averaged data recorded at the same sample rate as the first ADCP. Using the variance method, Reynolds stresses were estimated from the two ADCP datasets and compared with stresses computed directly from the velocity records obtained with a pair of ADVs co-located with the ADCPs. Both mode 1 and mode 12 stresses compare well with ADV derived stresses, however the mode 12 ADCP exhibits much lower instrument noise than the mode 1 ADCP. The lower noise floor associated with the mode 12 ADCP suggests that the variance method may be used with mode 12 to resolve smaller stresses than would be possible with mode 1.
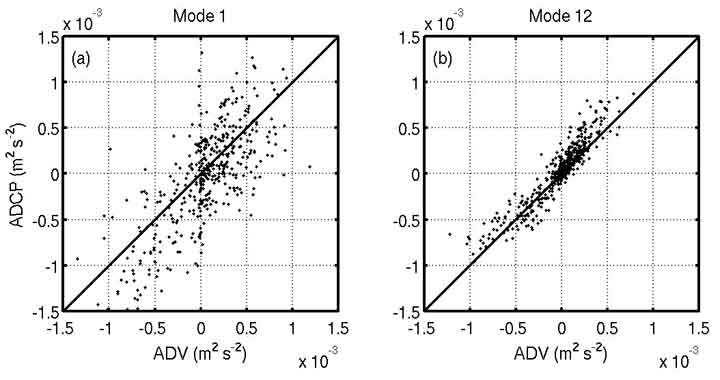
Comparison of along-channel Reynolds stresses derived from co-located ADV and ADCPs. Solid line through each plot represents a 1:1 ratio. (a) Mode 1, slope = 1.20±0.09, r^2 = 0.66 (b) Mode 12, slope = 1.01±0.04, r^2 = 0.86.